Credit : NASA / WMAP/ Wikimedia Commons
How the universe began? The answer is universe popped out from nothing. Yes. It just came out from nothing. That is what, the great ‘Big Bang’ theory suggests (not the TV show). 'Nothing' means there was absolutely nothing. No space and no time. Time itself started from Big Bang. But what in the world, triggered the Big Bang?
First thing you should know is, there is no OUTSIDE for our universe. The space and time exists within our universe itself and they came into existence after the Big Bang. So, the question what caused the Big Bang posses a serious issue of causality. There was no BEFORE to the event, Big Bang.
The word Big Bang misleads the public as it was an explosion in space. But it's not true, it was actually the appearance of space everywhere in the universe. It was a rapid expansion of space, analogous to the inflation of a balloon.
Now lets see the events happened in the beginning. The first event, modern physics is capable to understand, happened at hundredth of a billionth of a trillionth of a trillionth of a second after the Big Bang. That is too small. This time is called a Planck Time (10-43 sec). No one knows what happened before and has less idea during the Plank Time, after the Big Bang. Einstein’s General Relativity suggests, there was Gravitational Singularity before this time.
All the ideas about the very early universe are speculations. We don’t have sufficient insights about those time.
Early Universe
- Plank era (10-43sec) to Quark era (10-06sec)
Credit : Cern
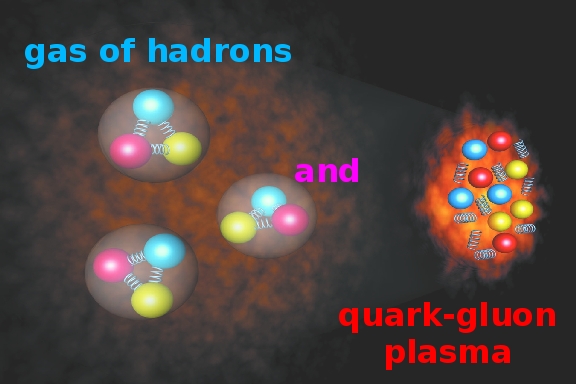
At Plank era, the four fundamental forces (electromagnetic force, weak and strong nuclear force and gravity) all had the same strength, and acted like a single fundamental force, held together by a perfect symmetry. At this time the Universe was expanded to a length of only 10-35 metres (Planck Length) and had a temperature of enormous 1032°C (Planck Temperature). The universe was an infinitely dense, hot fireball.
10-43 sec to 10-36 sec - gravity separated from the fundamental force and leads to creation of the earliest elementary particles (Quark-Gluon plasma or the "quark soup").
10-36 sec to 10-32 sec - the strong nuclear force separated and triggered the rapid exponential expansion of the universe, which is known as Cosmic Inflation.
10-32 sec to 10-12 sec - leads to the formation of Exotic particles like WIMPs (Weakly interacting massive particles, the fundamental particles of Dark Matter), neutrinos, Higgs Bosons etc.
10-12 sec to 10-06 sec - all fundamental forces become distinct and took their present form. Quarks, electrons, neutrinos etc were formed. Quarks and antiquarks annihilate each other on contact. But a quark for every billion pair survived from annihilation, thus forming the building block of matter.
Formation of Basic Particles
- Quark era (10-06sec) to Nucleosynthesis (20 mins)
Credits : uoregon.edu
At this time period, the universe cooled down and became less dense. The elementary particles smashed together leading to the formation of nuclei.
10-06 sec to 1 sec - quarks smashed each other to form hadrons (protons, neutrons etc). Electrons collided protons to give neutrons and massless neutrinos.
1 sec to 3 mins - leptons (electrons) and antileptons (positrons) collide each other and annihilate and that lead to release of energy in the form of photons.
3 mins to 20 mins - temperature again fell down. Nuclear fusion started and formed atomic nuclei of hydrogen, helium, lithium etc.
Formation of Atoms and Elements
- Nucleosynthesis (20 mins) to Dark Age (150 million years)
Credit : naoj.org
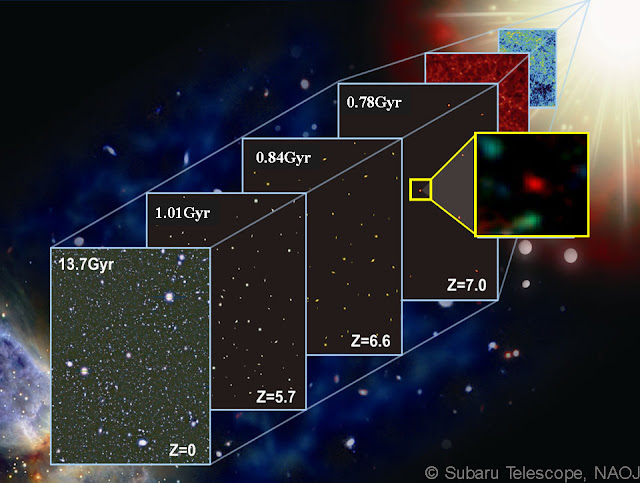
The temperature of the universe fell down again to the temperature of the surface of sun. Elements were created but still no activities of star creation occurred. Cosmic Background Radiation, we see today, started to emit.
3 mins to 240,000 years - universe was a breeding ground of nuclei, and was plenty with plasma of atomic nuclei and electrons. The energy of the universe was mainly from photons which interacted with, protons, neutrons and nuclei.
240,000 years to 300,000 years - formed the first atoms after nuclei captured electrons to neutralise. Universe become transparent to light, photons started travelling freely.
300,000 years to 150 million years - this period is called as the dark age, it is time period between the formation of atoms to the formation of first stars. Universe was dominated by Dark matter.
Formation of Stars and Galaxies
- Dark Age (150 million years) to Present Day (13.8 billion years)
Credit : universoracionalista.org
This was the period of quasars, stars, galaxies, black holes, neutron stars, supernovae and everything we see today. Universe continues to expand rapidly.
150 million years to 1 billion years - quasars began to form due to gravitational collapse and the universe was composed of ionised plasma. Started formation of stars and due to gravity, formed galaxies and clusters and superclusters of galaxies.
8.5 billion years to 9 billion years - Late generation star, sun was formed from the debris of many generations of stars and the solar system around it formed around 4.5 to 5 billion years ago.
Today, 13.8 billion years - to be exact 13.799±0.021 billion years from the Big Bang. The universe is still expanding and a vast breeding ground of celestial objects.
We have no idea how vast the Universe is and still lots of surprises to be found out, that the mighty Universe holds.



No comments:
Post a Comment